Forest cover up in Telangana, says FSI
In Indian State of Forest Report, 2019, it says the forest cover of Telangana has increased due to afforestation drive carried out by State government

Hyderabad: The State government’s flagship programme – Telangana Ku Harita Haram – has come in for high praise in the Indian State of Forest Report (ISFR), 2019, a biennial report brought out by Dehradun-based Forest Survey of India.
The report said Telangana State has recorded improvement in forest cover in all four categories – very dense forest, moderately dense forest, open forest and scrub. It said this was due to the afforestation programme envisaged to plant and protect 230 seedlings over a period of four years.
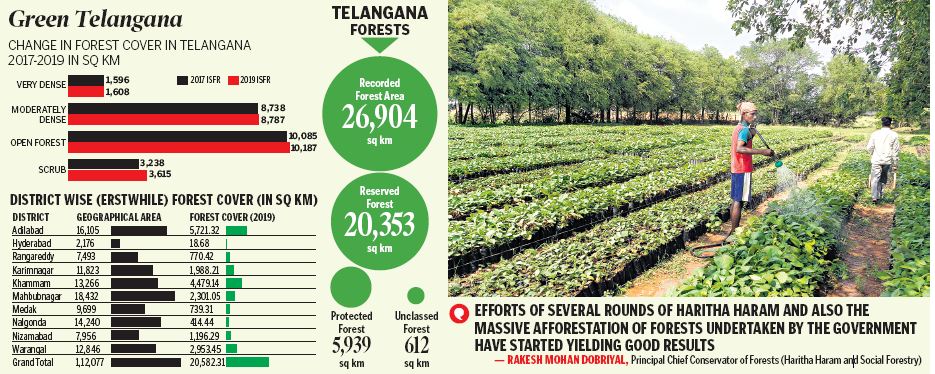
Based on the interpretation of IRS Resourcesat-2 LISS III satellite data of the period November 2017 to January 2018, in terms of forest canopy density classes, the State has 1,608.24 sq km under Very Dense Forest (VDF), 8,787.13 sq km under Moderately Dense Forest (MDF) and 10,186.94 sq km under Open Forest (OF). Forest cover in the State has increased by 163.31 sq km compared to previous assessment reported in ISFR, 2017.
Reacting to the report, Rakesh Mohan Dobriyal, Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (Haritha Haram and Social Forestry) told Telangana Today: “Efforts of several rounds of Haritha Haram and also the massive afforestation of forests undertaken by the government have started yielding good results. Actually, the forest land which is being taken for construction of irrigation projects has been compensated elsewhere on waste lands that otherwise would have remained barren. The impact of the present day ongoing afforestation programme, I am confident. will reflect the correct picture in the ISFR, 2021.”
Green wash
The survey says that Telangana had reported extent of Recorded Forest Area (RFA) as 26,904 sq km which is 24 per cent of its geographical area. The reserved, protected and unclassed forests are 75.65 per cent, 22.07 per cent and 2.28 per cent of the recorded forest area in the State respectively. Main reasons for the increase in forest cover in the State are plantation and conservation activities as well as improvement in interpretation, the report said.
Telangana forests
Telangana covers an area of 1,12,077 sq km, which is 3.41 per cent of the geographical area of the country. The State is endowed with rich diversity of flora and fauna. The State has dense teak forests on the northern part along the banks of river Godavari. As per the Champion and Seth Classification of Forest Types (1968), the forests in Telangana belong to three forest type groups, which are further divided into 12 forest types.
“The State Government has taken up a massive greening programme, ‘Telangana Ku Harita Haram’ in the State that aims at achieving the twin objectives of increasing the forest cover and reduce pressure on the existing forest resources, through massive community participation by Vana Samrakshana Samithis (VSS) and Eco-Development Committees (EDCs) in protected areas and Watershed Development Committees in the watershed areas,” the ISFR 2019 said.
Non Forest purposes
Recorded Forest Area (RFA) in the State is 26,904 sq km of which 20,353 sq km is Reserved Forest, 5,939 sq km is Protected Forest and 612 sq km is Unclassed Forests. In Telangana, during the period January1, 2015 to February 5, 2019, a total of 9,420 hectares of forest land was diverted for non-forestry purposes under the Forest Conservation Act, 1980. However during the last two years, 12,730 hectares of plantations including avenue plantations were undertaken in the State. Three national parks and nine wildlife sanctuaries constitute the protected area network of the State covering 5.08 per cent of its geographical area.
Tree cover
Trees occurring in patches of size less than one hectare including scattered trees are assessed through sampling based methodology. Tree cover in Telangana has decreased by 155 sq km as compared to the previous assessment reported in ISFR 2017. On the other hand the total Carbon stock of forests in the State including the Trees Outside Forests (TOF) patches which are more than 1 hectare in size is 151.84 million tonnes which is 2.13 per cent of total forest carbon of the country. Forest carbon stock is the amount of carbon that has been sequestered from the atmosphere and is now stored within the forest ecosystem, mainly within living biomass and soil, and to a lesser extent also in dead wood and litter.
As per the survey, the top five tree species in TOF (Rural) in Telangana, are Mangifera indica (Mango), Azadirachta indica (Neem), Butea frondosa (Moduga), Acacia Arabica (Tumma), Borassus flabelliformis (Palm). And the top five tree species in TOF (Urban) in Telangana are Azadirachta indica, Mangifera indica, Leucaena leucocephala (Tamarind), Tectona grandis (Teak) and Pongamia glabra (kanuga), but the same noted that forest land has been diverted for non forest purposes in certain areas during the period of 2017-2019.
Now you can get handpicked stories from Telangana Today on Telegram everyday. Click the link to subscribe.
Click to follow Telangana Today Facebook page and Twitter .
Related News
-
Telangana sets up Rythu Discom, liabilities of Rs 71,964 crore shifted
-
Telangana ranks 7th in NITI’s Fiscal Health Index for 2023-24, reflects BRS’ strong policies
-
Hyderabad cybercrime cracks down on 124 social media accounts promoting online betting
-
Hyderabad: Moving car catches fire on DRDL road near Chandrayangutta
-
Sports briefs: Indian boxers shine on day four at World Boxing Futures Cup
2 hours ago -
Nikki Pradhan achieves another milestone, completes 200 international caps
2 hours ago -
Iran targets ships, Dubai airport in Gulf escalation
3 hours ago -
FIH Qualifiers: India scores big win against Wales, storm into semifinal
2 hours ago -
India allows FDI under automatic route for firms with less than 10 per cent Chinese stake
3 hours ago -
IEA agrees to record emergency oil release to calm global prices
3 hours ago -
SFI students protest alleged ABVP attack in HCU hostel
3 hours ago -
Godrej Enterprises hosts GeeVees Awards 2026 to honour architects and designers
3 hours ago




